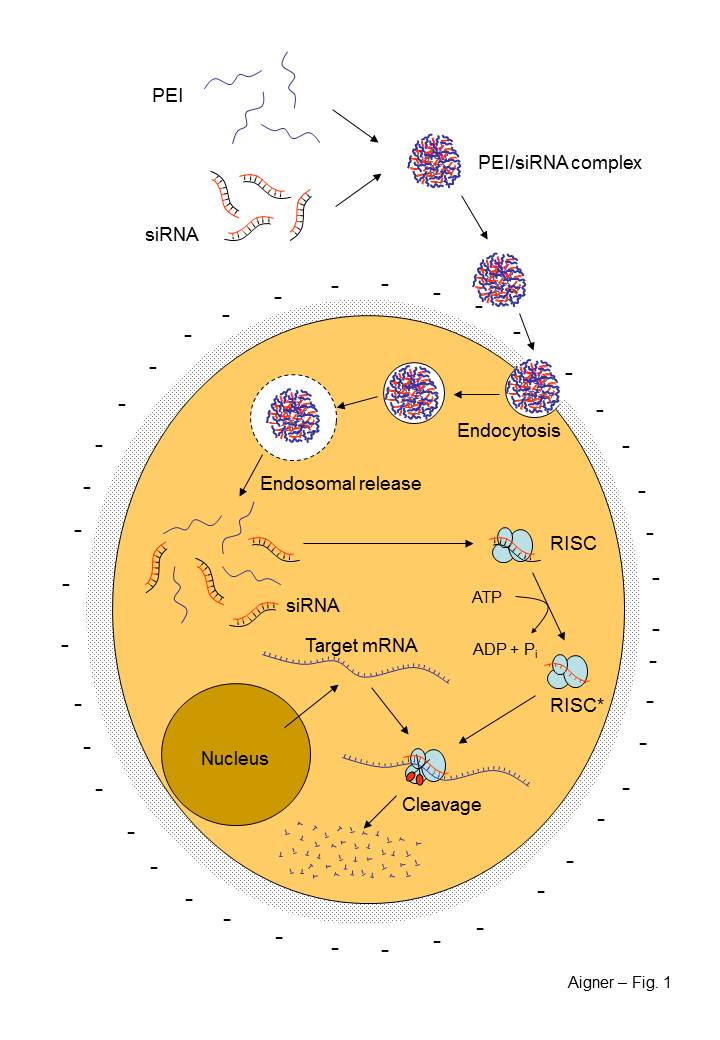
Model
of the PEI-mediated siRNA
delivery
(Aigner, Curr.
Opin. Mol. Ther., 2007
siRNA nanoparticlesPolyethylenimine (PEI)/siRNA complexes for RNAi-mediated therapeutic gene targeting in vivoRNA interference (RNAi) is a recently discovered method which allows the highly specific and very efficient silencing of any target gene. Thus, it offers great potential for in vitro target validation as well as in vivo as a novel therapeutic strategy. Since it relies on small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) acting as mediators of RNAi-induced mRNA degradation, the main issue for in vivo use of RNAi is the delivery of catalytically active siRNAs. In vivo, the direct application of siRNAs without chemical modifications is severely limited by their instability and poor delivery into target tissues. Most desirable is the direct, non-viral administration of siRNAs through systemic or local application. Polyethylenimines (PEIs) are synthetic polymers with a protonable amino group in every third position and a high cationic charge density. This allows the formation of non-covalent interpolyelectrolyte complexes ('nanoplexes') with nucleic acids. We develop nanoplexes based on PEIs as an efficient delivery platform for RNAi in vivo. The complexation of chemically unmodified siRNAs with various PEIs leads to the complete protection of siRNAs from nucleolytic degradation. |
|
|
|
Furthermore, certain PEIs mediate the highly efficient cellular uptake of siRNAs which, upon their intracellular release, display bioactivity already at low concentrations In various mouse tumor models, we explore PEI/siRNA nanoplexes for in vivo gene silencing. This includes different target genes, PEIs, tumor entities, and modes of administration. In ovarian carcinoma, glioblastoma, lung carcinoma, melanoma, pancreas and prostate carcinoma xenografts, we show the efficacies and biological effects of PEIs for in vivo siRNA delivery by targeting different tumor-relevant proteins. The systemic administration of PEI/siRNA nanoplexes, but not of naked siRNAs, allows the delivery of the intact siRNAs into different organs including tumors. |
|
|
|
This results in the specific downregulation of the target gene expression on mRNA and protein levels and in significant anti-tumoral effects.
|
|
|